
Our one byte checksum example could have been calculated with the following function (in C language) that we call repeatedly for each byte in the input string. In fact checksum calculations as described above can be defined in this way. Use a function F(bval,cval) that inputs one data byte and a check value and outputs a recalculated check value. The idea behind a check value calculation is simple. So calculating a checksum may be a simple method for detecting errors, but doesn’t give much more protection than the parity bit, independent of the length of the checksum. Even if we had used a four byte long checksum we would not have detected this transmission error. The checksum for this new string is still 210, but the result is obviously wrong, only after two bits changed. The receiver will than see the array representing the string “ M`mmert“. Let us assume that in our example array the lowest significant bit of the character ‘ L‘ is set, and the lowest significant bit of character ‘ a‘ is lost during communication. They often fail in bursts, or due to electrical spikes. In practice, bits do not change purely random during communications. Seems rather good, but this is only theory. We might conclude that with a four byte checksum the chance that we accidentally do not detect an error is less than 1 to 4 billion. Using a two byte checksum will result in 65,536 possible different checksum values and when a four byte value is used there are more than four billion possible values. In this example we have used a one byte long checksum which gives us 256 different values. You can use the calculator above to check this result. The one byte checksum of this array can be calculated by adding all values, than dividing it by 256 and keeping the remainder.

The example string is “ Lammert” which converts to the ASCII values. Lets take an example string and calculate a one byte checksum. It is certainly easier to calculate a checksum, but checksums do not find all errors. One might think, that using a checksum can replace proper CRC calculations. The answer is simple, they are powerful, detect many types of errors and are extremely fast to calculate especially when dedicated hardware chips are used. So let’s see why they are so widely used. Modern computer world cannot do without these CRC calculation. Also each data block on your hard-disk has a CRC value attached to it. All packets sent over a network connection are checked with a CRC. Nowadays CRC calculations are used in all types of communications.
The CRC calculation or cyclic redundancy check was the result of this. This website is also capable to calculate CRC-32, but keep in mind, CRC-32 is NOT used in RTU modbus.
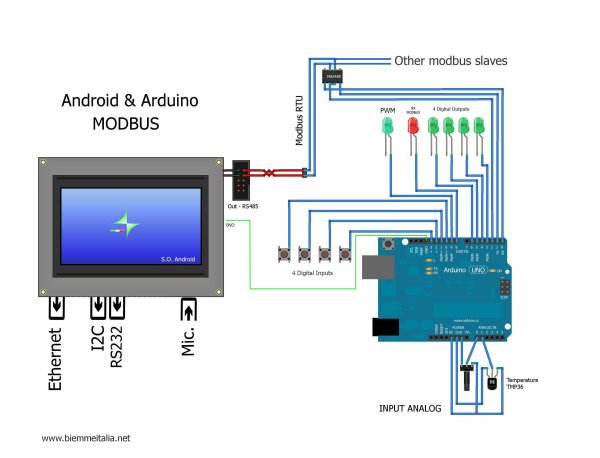
ARDUINO CRC16 MODBUS CODE
You can implement CRC-16 calculation in your codes ( Code 1) or calculate CRC one by one on the following website. It is really important since CRC-16 is added to the end of an RTU frame. To overcome this problem people have searched for mathematical sound mechanisms to detect multiple false bits. CRC-16 calculation generates 2 bytes from a datastring. This simple detection mechanism works if an odd number of bits in a byte changes, but an even number of false bits in one byte will not be detected by the parity check.

ARDUINO CRC16 MODBUS SERIAL
For serial data they came up with the solution to attach a parity bit to each sent byte. Since the beginning of computer science, people have been thinking of ways to deal with this type of problem. Whenever digital data is stored or interfaced, data corruption might occur.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
